
Tam's Bio 3.3a Insect Pollination
Pollination by insects probably occurred in primitive seed plants, reliance on other means being a relatively recent evolutionary development. Reasonable evidence indicates that flowering plants first appeared in tropical rain forests during the Mesozoic Era (about 65 million to 225 million years ago). The most prevalent insect forms of the period were primitive beetles; no bees and.

What is Pollination? Bee City Canada
Diagram illustrating the process of pollination Female carpenter bee with pollen collected from a night-blooming cereus. Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example beetles; birds, butterflies.
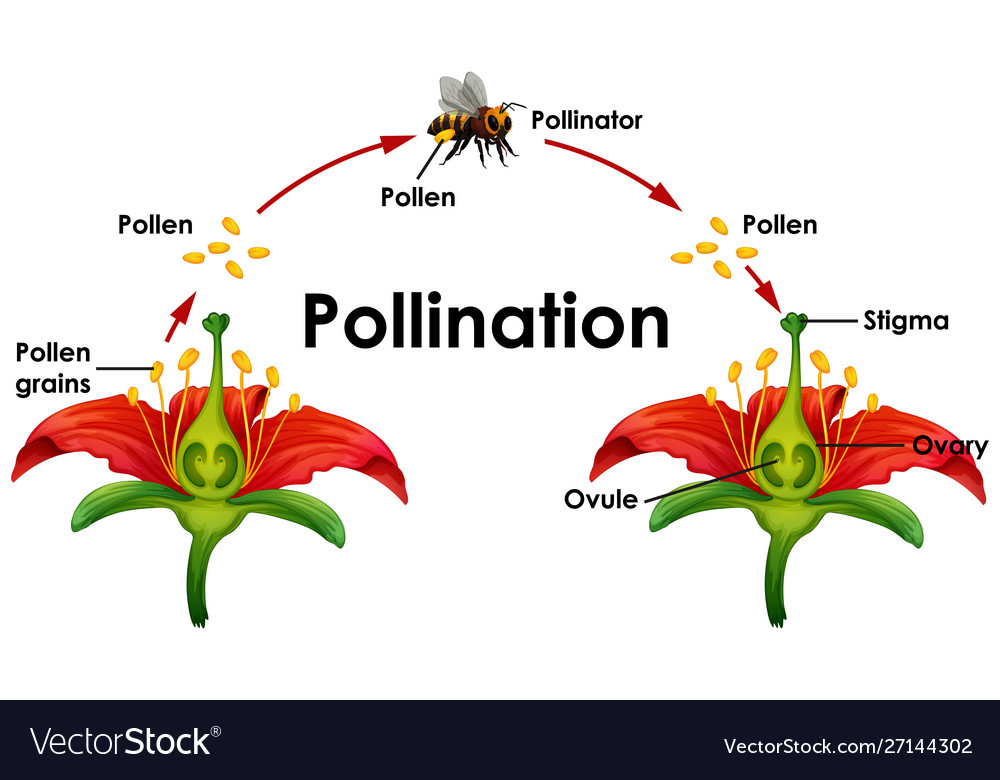
Diagram showing pollination with flower and bee Vector Image
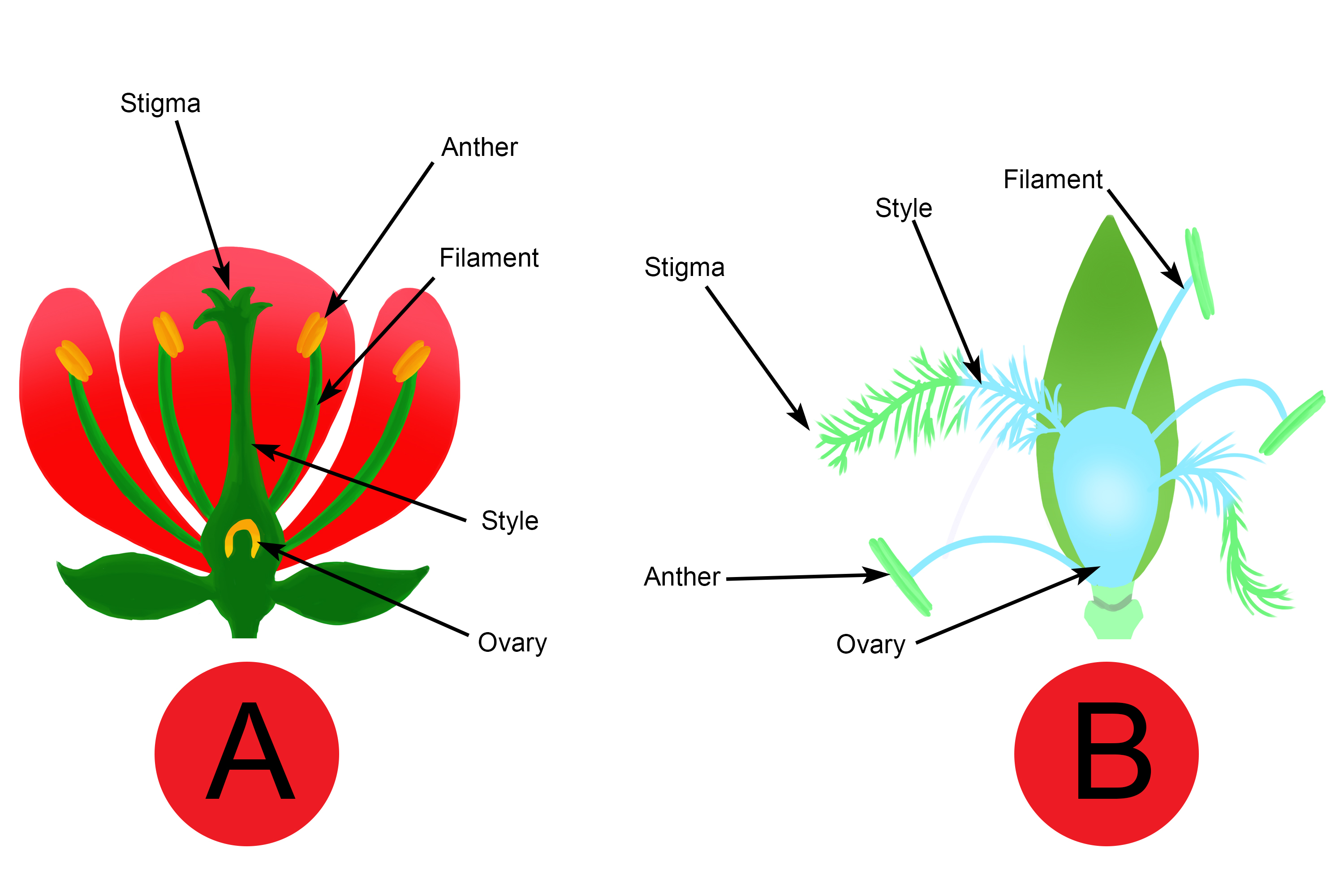
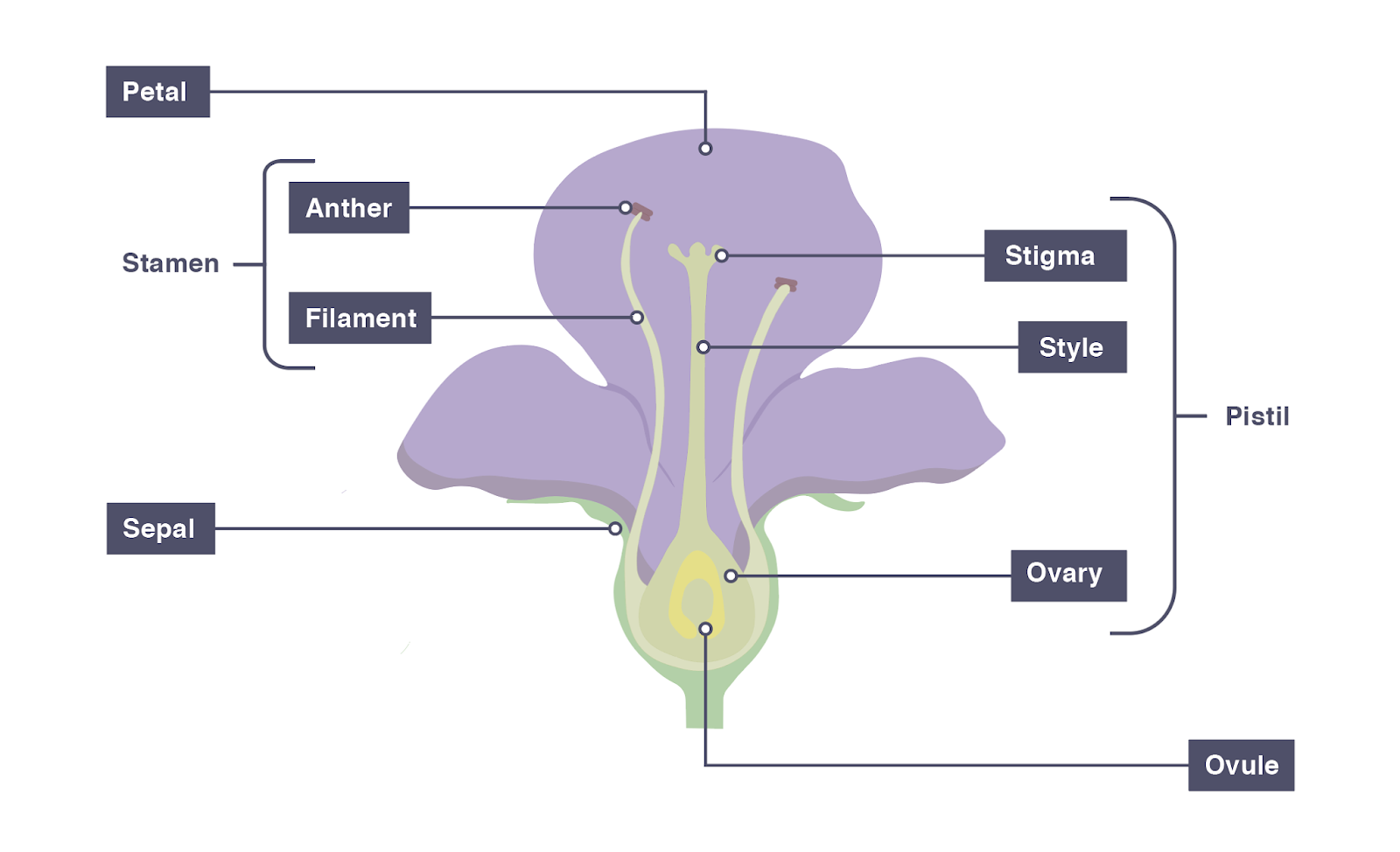
DIAGRAM: Insect pollinated flower 4.5 (2 reviews) + − Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by Vanita_KAUR4 Teacher Terms in this set (10) Term Anther Definition Site of pollen grain production. Part of the stamen. Location Term Stigma Definition Part of the female reproductive organs.
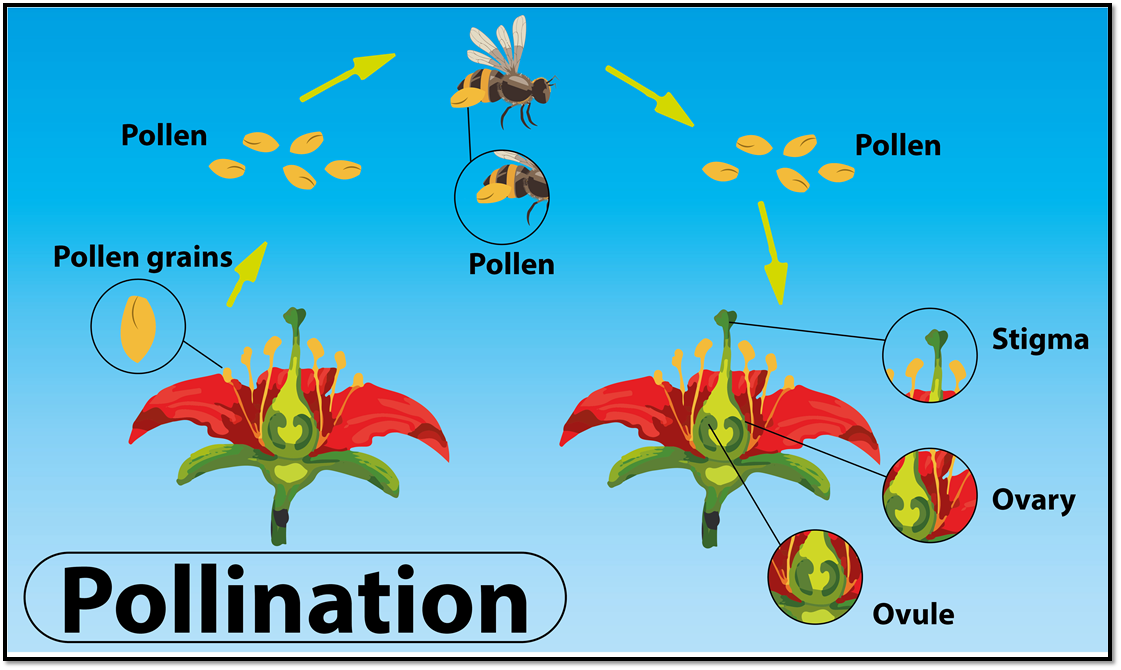
Pollination Process For Bees
What is pollination? Pollination can be defined as the natural process of transferring pollen grains from the anther (male reproductive part) to the stigma (female reproductive part) of a flower. This process can be carried out either within a flower or between flowers of the same or different plants. Explore more: Pollination

pollination. Honey bee is an animal of pollinator, flower, and pollen
Pollinator Insects. Insects typically pollinate flowers as they move from plant to plant searching for food. Many flowers produce nectar, a sugary liquid that many insects eat. When an insect lands on a flower to feed, pollen grains stick to its body. As the insect moves to another flower of the same species, these pollen grains are transferred.

Parts of the flower where bees need to collect and deposit pollen for
The diagram provided shows how a pollinator pollinates a plant, which means that it transports the male sex cells contained in pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of either the same or another flower.. Well, insect-pollinated flowers tend to have especially large and brightly colored petals, which advertises that this flower.
Question examples of which flower gets pollinated by what
LINKS:Worksheet and posters:https://igcsebio.sciencesauceonline.com/flower-structures-and-functions/RELATED VIDEOSHow to Draw a Flower: https://youtu.be/4XgS.

Pollinating Plants With Insects And Selfpollination, Flower Anatomy
Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology: Reproduction - Specification point - 3.3 describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and a wind-pollinated flow.

iGCSE Biology Diagrams Flower (Insect pollinated) No2 Diagram Quizlet
Find the deal you deserve on eBay. Discover discounts from sellers across the globe. We've got your back with eBay money-back guarantee. Enjoy Flowers chart you can trust.
Pollination Science, Plants, Environment ShowMe
There are two types of pollination: Self-pollination: The pollen grain lands on the same flower it originated from. Cross-pollination: The pollen grain lands on a different flower to the.
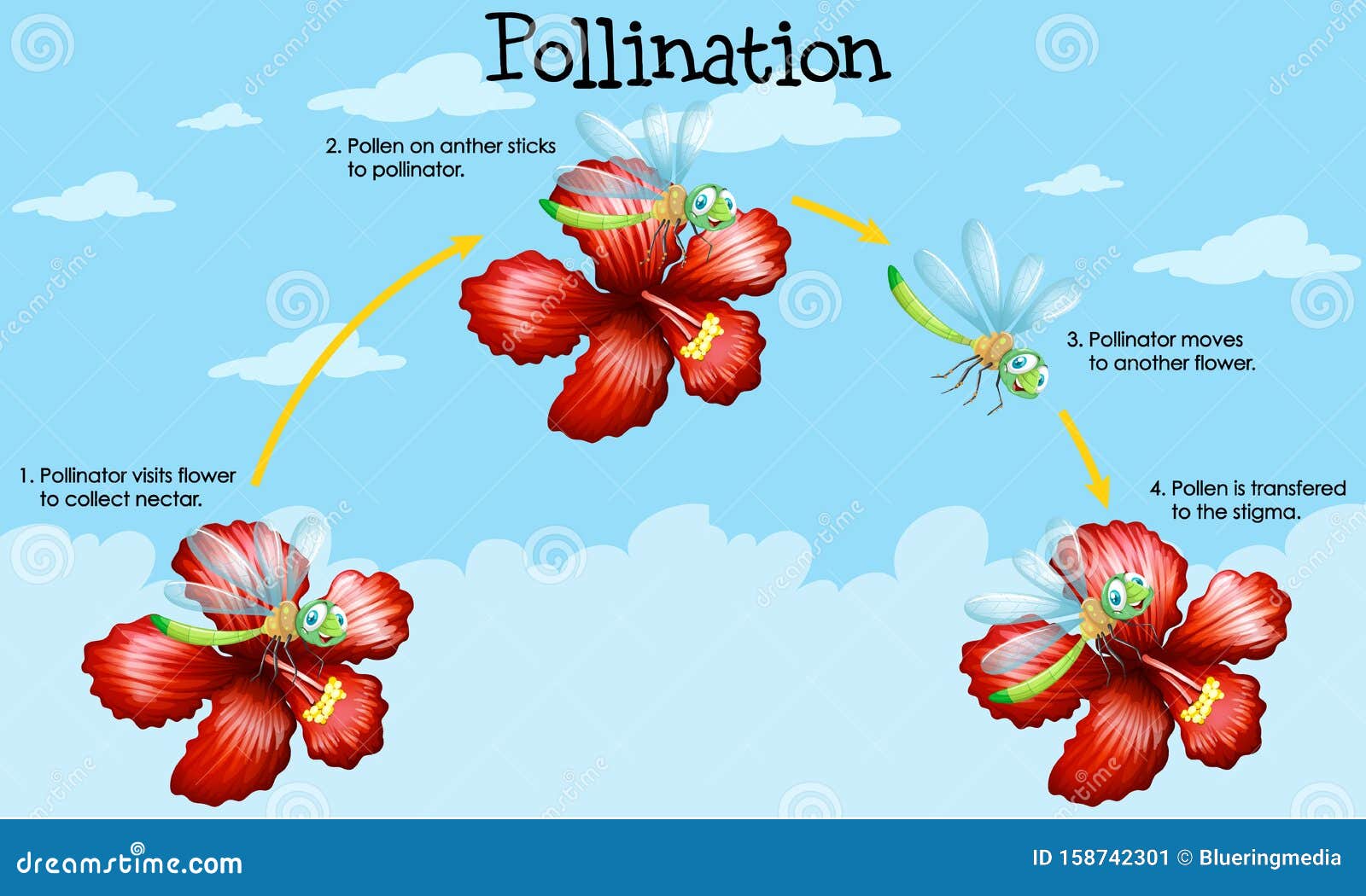
Diagram Showing Pollination with Flowers and Bugs Stock Vector
Many flowers will remain unpollinated, failing to bear seeds if honeybees disappear. The impact on commercial fruit growers could be devastating. Figure 32.5.1 32.5. 1: Pollination by insects: Insects, such as bees, are important agents of pollination. Bees are probably the most important species of pollinators for commercial and garden plant.
IGCSE Biology 2017 3.3 Describe the Structure of an Insect
The structures of an insect-pollinated flower ensure that the flower is well-adapted for pollination by insects; Features of an Insect-pollinated Flower Table.. Genetic Diagrams; 3.24 Family Pedigrees; 3.25 Predicting Probabilities of Outcomes from Monohybrid Crosses; 3.26 Sex Chromosomes;

The world of plants and flowers Pollination by insect
Topic Pollination in plants Level GCSE (or any course for students aged 14-16) Outcomes 1. To describe and explain adaptations of wind, insect and mammal pollinated plants . 1. Label the wind pollinated flower above. 2. Compare the structures of insect and wind pollinated flowers . (Use correct comparative language. See box below for support) 3.
.PNG)
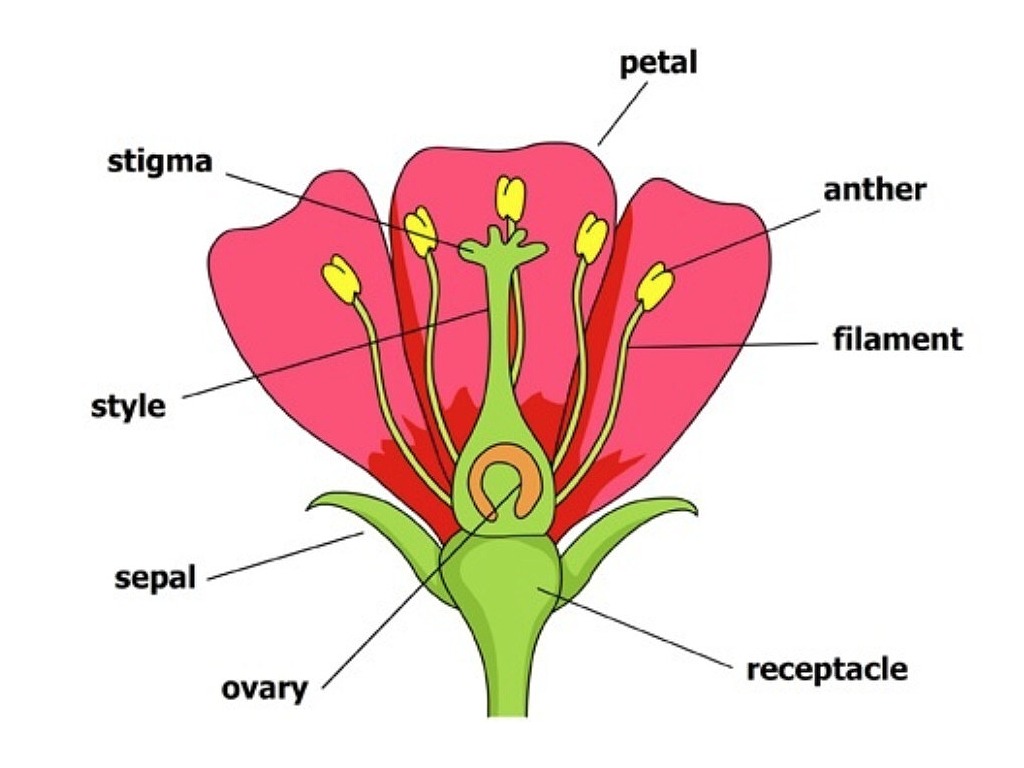
Structure of a Flower
Unlike the typical insect-pollinated flowers, flowers adapted to pollination by wind do not produce nectar or scent. In wind-pollinated species, the microsporangia hang out of the flower, and, as the wind blows, the lightweight pollen is carried with it (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). The flowers usually emerge early in the spring, before the.

Plant for Pollinators Plant Something MA Plant Something MA
Show your loved ones unconditional affection. Beautiful flower bouquets for any occasion! Enjoy our hand-selected, beautifully curated blooms delivered to your door. Shop online!
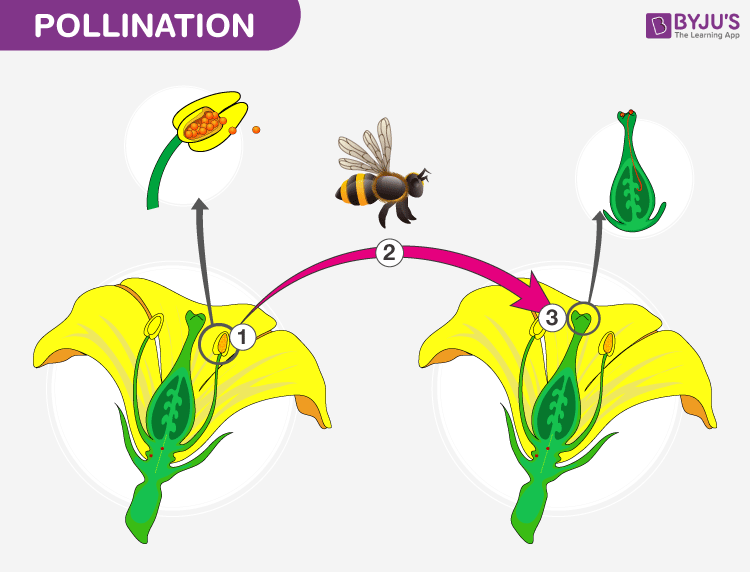
Pollination Introduction, Process and Types of Pollination
Sneezeweed Common sneezeweed | image by USFWS Mountain-Prairie via Flickr Scientific name: Helenium autumnale Sneezeweed is a plant that produces yellow flowers that resemble daisies. It's one of the lovely flowers that you might observe being pollinated by a large number of insects.